Credit report summary
A guide to understanding the information in your credit report
What is in your credit report?
Your credit report is a record of your credit history. It includes information to identify you as well as information about your credit history, including loans you've applied for and taken out. You can access your credit report free of charge every three months.
Note: This is a summary of what can be shown in your credit report. Each credit reporting body may display this information in a different format.
Personal Information
This section shows the personal information that is used to assist in identifying you:
- Name
- Gender
- Date of birth
- Driver’s licence
- Employer
- Current Address/address history

 2
2
Credit Rating
Your credit rating is shown inside a range and on a scale (e.g. 'below average' to 'excellent'). Some credit reporting bodies will also give you a credit score.
Credit Account Information
Details about the credit accounts that you have opened, or had open in the last 2 years, including:
- the type of credit account (such as credit card, home loan, personal loan)
- the credit limit
- the credit provider
- dates the accounts were opened and closed
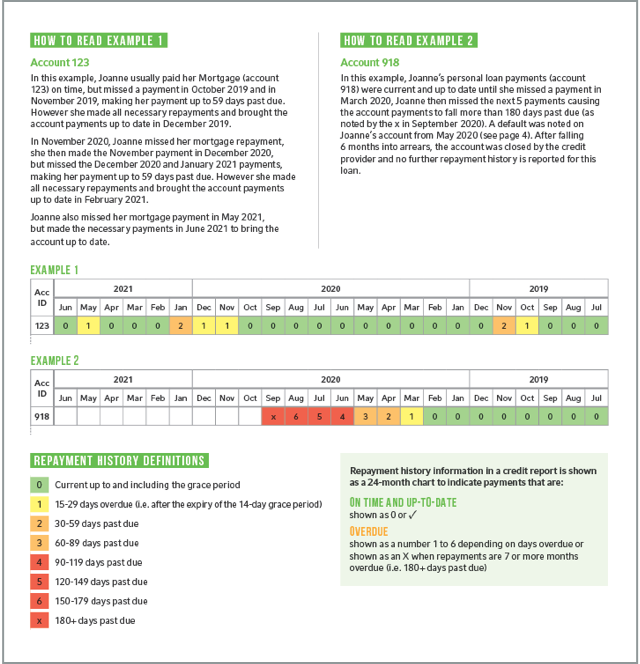
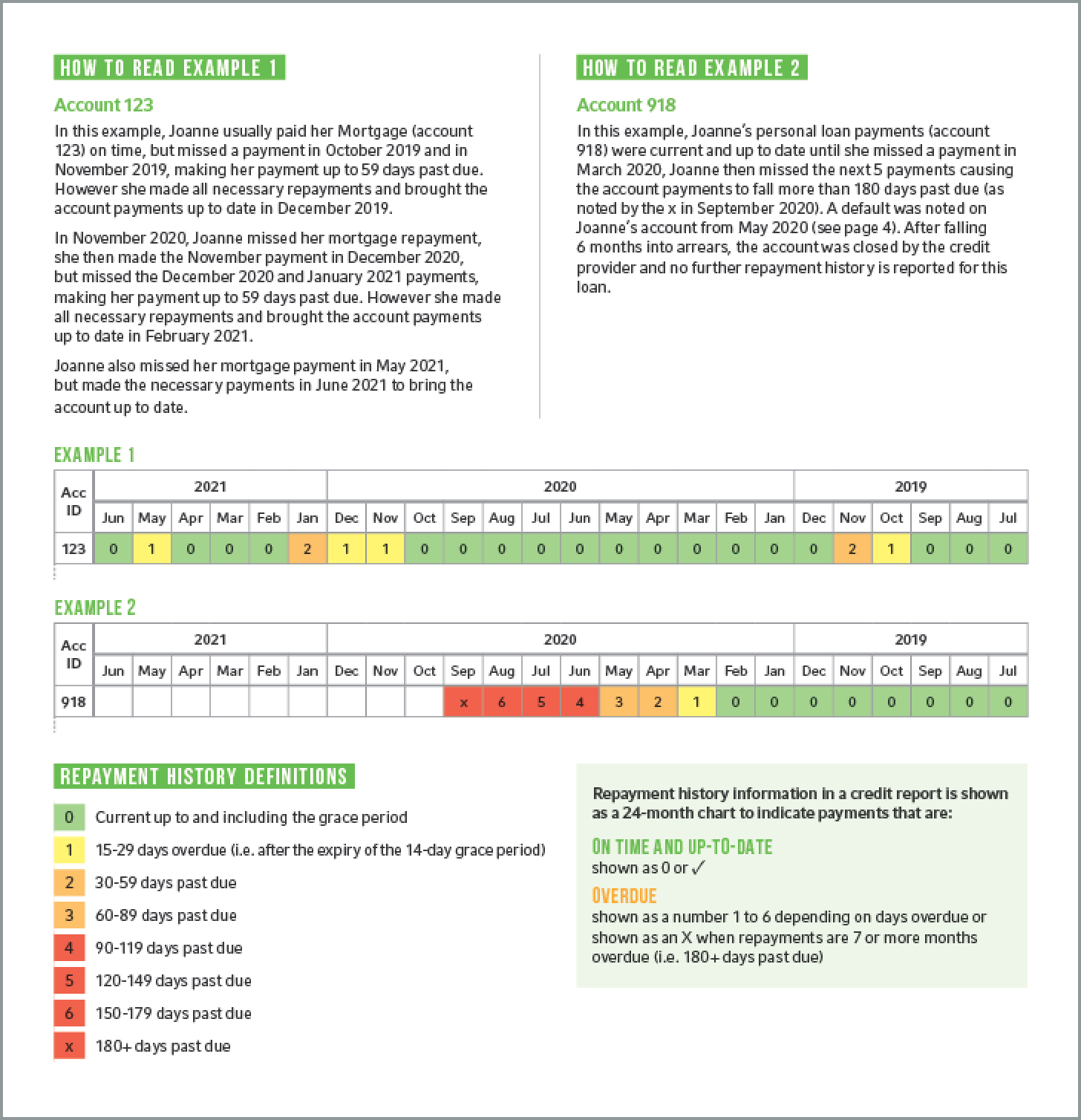
Repayment History Information
Information about your repayment history for your credit accounts - that is, whether you've made your payments on time. This is very important information, because if you apply for a loan with a new lender, it tells them how well you've managed your existing loans. Your repayment history information is recorded on a month-by-month basis (after 24 months, the information is removed from your credit report).
Only banks, credit unions and other types of finance companies can report or access repayment history information. Phone, gas and electricity providers are not able to report or access this information. This means that your credit report will not show whether you've paid your phone or utility bills on a month-by-month basis.
A 'grace period' of 14 days is applied to the first overdue payment. During this time, a credit provider cannot report a late payment to a credit reporting body. If the amount owing is paid during the grace period, there will be no record on your credit report that you made a late payment. However, once the grace period has passed, if you have not made the full payment of the amount owing, the credit provider may report this as a late payment to the credit reporting bodies.
Financial Hardship Information
A financial hardship arrangement is an agreement between you and your lender to adjust or defer your loan repayment obligations because something has happened which has had an impact on your ability to repay. A natural disaster is an example of when this might happen, but other circumstances such as illness, job loss or relationship breakdown might also lead to such an outcome.
Financial hardships arrangements in respect to loans like credit cards, home loans, personal loans and car loans can appear on the credit report. Hardship arrangements with phone, internet and utility companies and buy-now-pay-later accounts will not appear on the credit report.
Financial hardship information is only retained on your credit report for 12 months, after which time the information is removed from your credit report.
There are two different types of financial hardship indicators that can be included in a credit report, depending on the type of arrangement you have agreed on with your lender:
![]() reflects a temporary arrangement or deferral
reflects a temporary arrangement or deferral
![]() reflects a permanent change and the loan is varied
reflects a permanent change and the loan is varied
The examples below are common scenarios to help you understand how this may impact your credit report:
Temporary Financial Hardship Arrangement
Short-term relief from or deferral of payment obligations, which will be marked as ![]() on the credit report. The
on the credit report. The ![]() will be reported for the number of months the arrangement is in place. If you make the agreed repayments on time, your repayment history
information will show as up to date (ie.
will be reported for the number of months the arrangement is in place. If you make the agreed repayments on time, your repayment history
information will show as up to date (ie. ![]() or
or ![]() )
and will include an
)
and will include an ![]() (a grace period does not apply during a temporary financial hardship arrangement).
(a grace period does not apply during a temporary financial hardship arrangement).
| Acc ID | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jun | May | Apr | Mar | Feb | Jan | Dec | Nov | Oct | Sep | Aug | Jul | June | May | Apr | Mar | Feb | Jan | Dec | Nov | Oct | |
| 235 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||
← Read dates from right to left
Variation Financial Hardship Arrangement
A permanent variation or change to the terms of a credit agreement, which will be marked as ![]() on the credit report. The
on the credit report. The
![]() will be reported only for the month that the variation takes effect. If you agreed to a variation financial hardship arrangement with your
lender, and you make the required repayments on time (or within the grace period), your repayment history information will show as up to date (ie.
will be reported only for the month that the variation takes effect. If you agreed to a variation financial hardship arrangement with your
lender, and you make the required repayments on time (or within the grace period), your repayment history information will show as up to date (ie. ![]() or
or ![]() ) and will include a
) and will include a ![]() .
.
| Acc ID | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jun | May | Apr | Mar | Feb | Jan | Dec | Nov | Oct | Sep | Aug | Jul | June | May | Apr | Mar | Feb | Jan | Dec | Nov | Oct | |
| 539 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||||
← Read dates from right to left
Temporary Financial Hardship Arrangement & Variation Financial Hardship Arrangement
Depending on your circumstances and your lender's approach to hardship, you may have an ![]() recorded on your credit report
during a temporary payment deferral followed by a more permanent variation to your contract (which will be shown by a
recorded on your credit report
during a temporary payment deferral followed by a more permanent variation to your contract (which will be shown by a ![]() ).
).
| Acc ID | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jun | May | Apr | Mar | Feb | Jan | Dec | Nov | Oct | Sep | Aug | Jul | June | May | Apr | Mar | Feb | Jan | Dec | Nov | Oct | |
| 539 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||
← Read dates from right to left
Defaults
Any defaults on consumer credit that a credit provider has listed about you.
- A default is a formal notification from your credit provider to a credit reporting body that you are 60 days or more overdue in making a payment on a debt where the outstanding amount due is at least $150.
- Before listing a default, the credit provider will have written to you at least twice to ask for payment, and you will be warned that they are about to list a default if you do not make a payment.
- A default stays in your credit report for 5 years. If you subsequently pay off the default, your credit report will be updated to show this - but the default will stay in the report for the 5 years.
Serious Credit Infringements
A serious credit infringement is a serious indicator of bad conduct by a debtor. It can indicate that the credit provider considers the debtor has acted fraudulently, such as lying about their financial situation when applying for the loan. Serious credit infringements stay on the credit report for 7 years.
It can also mean that the credit provider believes that the debtor has intentionally failed to comply with their credit obligations, such as moving address and failing to tell the credit provider. In this case, the credit provider has to have tried to contact the debtor for more than six months without success, including taking certain steps to establish contact with the debtor. This type of serious credit infringement can only be reported if the credit provider has first reported a default - however, it will be removed if the debtor subsequently pays the debt (although the default will remain for 5 years).
Credit Enquiries
Information about the applications for credit you've made, including the date of the application, the type of credit and the amount you applied for.
- It does not show whether the application was successful or not.
- Credit Enquiry information remains on your credit report for five years from the date of the application.
- Whether a credit report records a particular loan application will depend on whether the credit provider got a copy of your report from the credit reporting body when you applied.
Other types of enquiries
- In addition to the credit provider, some other businesses that are involved in the credit application can access your credit report, such as businesses that offer lender's mortgage insurance (which is insurance that protects the interests of the credit provider if you are borrowing money to buy a home without a big enough deposit).
- Your credit report will record these enquiries. These records are retained on your credit report for 5 years from the date of the enquiry.

Commercial Credit Information
An overview of the credit accounts, defaults, infringements, enquiries of any commercial credit accounts you (or a company of which you are a director) currently hold, or have held with a credit provider.
Public Record Information
The Public Record Information section shows information relating to your credit activity that comes from publicly available sources, including:
- Personal insolvency information, like bankruptcies and debt agreements.
- These records are retained on your credit report for different periods depending on the specific information type, but generally roughly between either 5 years from the date of bankruptcy or debt agreement or 2 years from the end of the bankruptcy of debt agreement (whichever is the later period).
- Credit-related court judgements about you.
- Information about company directorships you’ve held.
Access information
To ensure your privacy, when you get a copy of your credit report, it will list everyone who has accessed (i.e. looked at) your credit report. The law sets out who and for what purposes your credit report can be accessed. This includes:
- You (i.e. when you get your free credit report from credit reporting bodies).
- People and businesses that are acting on your behalf, like a mortgage broker or financial counsellor.
- Subscription websites that provide you with your free credit score, like creditsavvy.com.au, creditsimple.com.au and getcreditscore.com.au.
- Credit providers and their agents for permissible purposes – in addition to getting your credit report when you apply for a loan, a credit provider may access it for a few, strictly limited purposes such as helping them to collect overdue payments.
Your credit report may have one or more sections listing who has ‘accessed’ the report. This information is shown to you but is not shared with a credit provider and won't impact your loan applications.